Introduction to Virtual Classrooms
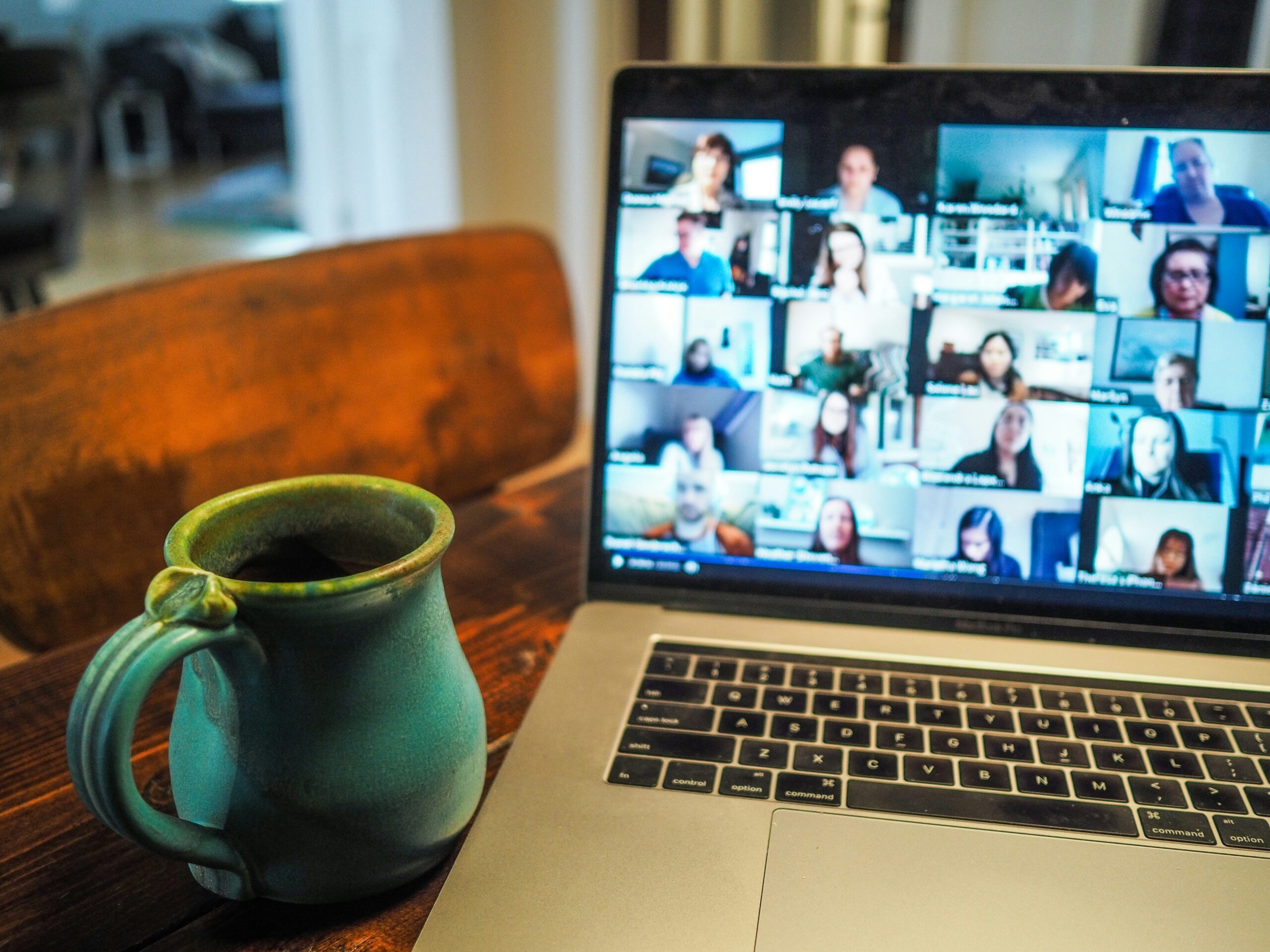
The concept of virtual classrooms represents a paradigm shift in modern education, revolutionizing how teaching and learning are conducted. Virtual classrooms function as digital environments where instructors and students interact in real time, utilizing the internet as their primary medium. This mechanism allows for flexible learning opportunities that transcend geographical boundaries, enabling learners from diverse locations to access quality education.
To participate effectively in a virtual classroom, certain technological requirements must be met. Students and educators typically need a reliable internet connection, a computer or tablet, and appropriate software designed for online education. These platforms, such as Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Classroom, provide essential features like video conferencing, screen sharing, and discussion forums, which are critical for effective communication and collaboration. With user-friendly interfaces and multi-device compatibility, these tools help facilitate an engaging learning experience.
The significance of virtual classrooms cannot be overstated in contemporary education systems. They provide unprecedented accessibility, allowing institutions to reach a broader audience and cater to varying learning needs. Particularly in response to global events that necessitate remote education—such as pandemics—virtual classrooms have proven essential in maintaining academic continuity. Furthermore, they offer opportunities for personalized learning experiences through adaptive technology, enabling instructors to tailor content to individual student needs. As educational institutions increasingly embrace this innovative approach, virtual classrooms are becoming a cornerstone of modern teaching methodologies.
Benefits of Virtual Classrooms
Virtual classrooms have revolutionized the educational landscape, offering a multitude of benefits to students, educators, and institutions alike. One of the most significant advantages is the flexibility in scheduling that virtual learning provides. Students can access course materials and participate in live sessions from anywhere with an internet connection, allowing them to tailor their learning around personal and professional commitments. This enhanced flexibility can lead to improved student satisfaction and retention rates.
Another notable benefit of virtual classrooms is the ability to reach a global audience. Traditional educational settings are often limited by geography, confining students to local institutions. However, virtual learning platforms break down these barriers, enabling institutions to attract a diverse range of students from different cultures and backgrounds. This global reach not only enriches the learning experience but also prepares students for a more interconnected world.
Furthermore, virtual classrooms allow for tailored learning experiences. Educators can employ various instructional methods—such as videos, quizzes, and interactive discussions—to cater to different learning styles. This customized approach ensures that all students, regardless of their preferred learning modes, can engage effectively with the material. Additionally, interactive tools facilitate greater student participation, enhancing overall engagement. For instance, features like polls, breakout rooms, and discussion boards can make learning more dynamic and collaborative.
Finally, virtual classrooms offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional education. Both institutions and learners can benefit from reduced operational and commuting costs associated with physical classrooms. Educational institutions can save on facilities and maintenance expenses, while students can mitigate costs related to transportation and accommodation. As a result, virtual classrooms present a sustainable model that optimizes educational delivery and access.
Challenges in Virtual Classroom Teaching
Virtual classroom teaching presents a range of challenges that affect both educators and students, making the transition from traditional teaching methods to online platforms a complex endeavor. One of the primary obstacles is the technological barriers that some users face. Not all students have access to high-speed internet or the necessary devices, which can significantly hinder their ability to participate fully in virtual lessons. This disparity in access to technology can exacerbate existing inequalities in education, leaving some students at a disadvantage.
Another significant challenge is the lack of personal interaction, which is often viewed as an essential component of effective teaching and learning. In a virtual classroom environment, the absence of face-to-face engagement can lead to feelings of isolation for students, impacting their motivation and participation. Educators also face difficulties in building rapport and understanding non-verbal cues that typically facilitate communication and learning in a physical classroom setting.
Distractions at home can further complicate the learning process in a virtual environment. Students may struggle to focus due to various interruptions, such as family members, pets, or household chores. These distractions can make it challenging for educators to maintain an interactive learning atmosphere, ultimately affecting the overall educational experience.
Lastly, evaluating student performance in a virtual classroom can be problematic. Traditional assessment methods may not translate well to an online setting, and educators may find it difficult to get an accurate representation of a student’s understanding and skills. This can lead to inconsistencies in grading and assessment, raising concerns about fairness and reliability.
The Role of Technology in Virtual Learning
The integration of technology in virtual classrooms has revolutionized the landscape of education, enhancing both teaching and learning experiences. The foundational infrastructure supporting virtual learning comprises a range of software and hardware tools that educators can leverage to optimize engagement and comprehension among students. Central to this is the selection of effective learning management systems (LMS), which serve as platforms for content delivery, assessment, and student interactions. Popular LMS options include Moodle, Blackboard, and Canvas, each offering unique functionalities that cater to different educational needs and preferences.
In addition to LMS, educators utilize various audiovisual equipment to support their virtual teaching methods. High-quality webcams, microphones, and speakers ensure clear communication and active participation in online classes. Furthermore, digital whiteboards and screen-sharing capabilities facilitate collaborative learning, allowing both instructors and students to illustrate concepts visually and engage in real-time discussions.
Moreover, the emergence of innovative educational technologies, such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), has the potential to deepen learners’ understanding of complex subjects. These technologies create immersive environments that can transport students to historical events, scientific phenomena, or artistic explorations, thus making the learning experience more interactive and engaging. The use of AR and VR in virtual classrooms can bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical applications, enhancing the retention of information.
The convergence of these technological tools fosters an inclusive and adaptable learning environment. Educators can cater to diverse learning styles and paces, ensuring that all students have an opportunity to succeed. By effectively utilizing these resources, the efficiency and effectiveness of virtual learning can be significantly amplified, thereby supporting the overall educational objectives of institutions.
Pedagogical Approaches for Virtual Classrooms
The transition to virtual classrooms necessitates the adoption of innovative pedagogical approaches to enhance the teaching and learning experience. Blended learning, which combines traditional face-to-face classroom strategies with online educational resources, is one of the most effective methods. This approach allows educators to provide a more personalized learning experience tailored to students’ individual needs. By leveraging technology, instructors can assign online modules that complement in-person interactions, thereby fostering a more engaged learning environment.
Another effective strategy is the flipped classroom model, where students first encounter new material online, typically through video lectures or reading assignments, before discussing it in class. This approach encourages students to take responsibility for their learning and enables educators to use class time for interactive activities such as discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative projects. In virtual settings, teachers can utilize video conferencing tools to facilitate these discussions, maintaining a rigorous curriculum while promoting deeper engagement with the content.
Project-based learning (PBL) is also particularly well-suited for virtual classrooms. This method encourages students to explore real-world problems and challenges through collaborative projects. By working in groups, students develop critical thinking and teamwork skills, while teachers act as facilitators rather than traditional lecturers. In an online environment, platforms like Google Workspace or collaborative tools such as Trello allow students to manage projects effectively, share resources, and communicate easily, making PBL highly adaptable for virtual learning.
In conclusion, implementing pedagogical approaches like blended learning, flipped classrooms, and project-based learning in virtual classrooms can significantly enhance educational outcomes. By embracing these methods, educators can cultivate a dynamic and interactive online learning experience that meets the diverse needs of their students.
Student Engagement and Interaction
Virtual classrooms have transformed the educational landscape by providing innovative methods to enhance student engagement and interaction. One critical aspect of maintaining student interest is the strategic incorporation of techniques and tools that promote active participation. Instructors can leverage gamification, a method that applies game-design elements in non-gaming contexts, to boost motivation and engagement. By incorporating competitive elements, rewards, and challenges, students can experience an interactive learning environment that fosters enthusiasm and involvement.
Another effective strategy is the use of breakout rooms. These smaller, more intimate virtual spaces enable students to collaborate on tasks, discuss concepts, and share insights with their peers in a more personal setting. This approach not only encourages students to actively engage with the course material but also facilitates the development of essential teamwork and communication skills. Instructors can rotate among the breakout rooms to provide support and facilitate discussions, further enhancing the interactive experience.
Polls and surveys are valuable tools that can gauge student understanding and ensure that learners are actively participating in discussions. By asking students to respond to questions during a live session, instructors can create a dynamic learning atmosphere while simultaneously providing immediate feedback on comprehension. Interactive assignments, such as quizzes and collaborative projects, can also maintain student engagement by challenging learners to apply their knowledge in creative ways.
Overall, employing a variety of interactive techniques in virtual classrooms can significantly enhance student motivation and participation. By fostering an environment that encourages active involvement, educators can ensure that students remain engaged and committed to their learning journey. The integration of these strategies not only enriches the educational experience but also cultivates a sense of community and collaboration among students.
Assessing Student Performance in Virtual Classrooms
In the realm of virtual classroom teaching, evaluating student performance presents unique challenges that diverge from traditional educational settings. The shift to an online learning environment necessitates adaptations in assessment methods to accurately gauge student understanding and engagement. Standard assessment techniques such as timed examinations may prove less effective in a virtual setting; thus, educators have begun to explore alternative strategies that align more closely with online learning dynamics.
Formative and summative assessments are two integral components of the assessment framework in virtual classrooms. Formative assessments, which occur during the learning process, allow educators to monitor student progress and identify areas needing improvement. Techniques such as quizzes, discussion board participation, and interactive polls serve as immediate feedback mechanisms, fostering a more responsive teaching approach. Conversely, summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of a course or unit, often taking the form of online tests or projects that measure cumulative knowledge and skills acquired throughout the instruction period.
The incorporation of feedback in the assessment cycle is crucial for enhancing student learning outcomes in a virtual classroom setting. Personalized feedback not only informs students of their performance but also provides actionable insights that guide their future learning efforts. Educators can utilize various tools, including video comments and written responses, to deliver constructive feedback that encourages self-reflection and improvement. Moreover, technology facilitates ongoing communication between instructors and students, enabling timely interventions when challenges arise.
Despite the advantages, assessing student performance in a virtual classroom is not without hurdles. Issues such as student motivation, academic integrity, and the technological divide can hinder effective assessment. Addressing these challenges requires a comprehensive understanding of each learner’s context, ensuring that assessments remain fair, valid, and reliable within an online environment. By leveraging innovative assessment strategies and emphasizing meaningful feedback, educators can successfully navigate the complexities of evaluating student performance in virtual classrooms.
Future Trends in Virtual Classroom Teaching
The landscape of virtual classroom teaching is continuously evolving, driven by advances in technology and changing educational needs. One of the most prominent trends is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into online learning environments. AI can analyze student performance, provide tailored recommendations, and facilitate real-time feedback. This shift allows educators to personalize learning experiences to suit individual requirements, enhancing engagement and improving educational outcomes. By leveraging AI technologies, virtual classrooms can better adapt to diverse learning styles and preferences.
Additionally, the personalization of learning experiences will likely become more pronounced. As educational platforms gather more data on student interactions, techniques such as adaptive learning will enable more customized curricula. This approach not only caters to students’ unique learning paths but also encourages autonomy and motivation in the learning process. The future will likely see the rise of platforms that utilize analytics to provide insights into students’ strengths and weaknesses, allowing for a more focused educational journey.
An emerging trend is the potential of hybrid models, which combine in-person and virtual classroom teaching. As schools and institutions seek to create more flexible learning environments, hybrid models allow for a seamless transition between traditional and online education. This approach can accommodate diverse preferences and circumstances, making education more accessible and inclusive for a wider range of learners. It also encourages collaboration and interaction among students, which can enrich the educational experience.
Finally, evolving educational policies will play a significant role in shaping virtual classroom teaching. As technology continues to influence the educational landscape, policy makers will need to address issues such as digital equity, data privacy, and teacher training. By establishing supportive frameworks for online education, stakeholders can ensure that virtual classrooms are effective, equitable, and aligned with 21st-century learning requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the rise of virtual classroom teaching via the internet has profoundly reshaped the landscape of education. This method provides unprecedented accessibility, enabling students from diverse backgrounds and geographical locations to engage with high-quality educational resources. By breaking down traditional barriers, such as location and financial constraints, virtual classrooms have democratized learning opportunities, creating a more inclusive environment.
Moreover, the technology inherent in online teaching platforms fosters interactive learning experiences. Through video conferencing, discussion forums, and collaborative tools, students can actively participate in their education, enhancing their understanding of complex subjects. These interactive features not only motivate learners but also cater to various learning styles, promoting a more personalized educational experience.
However, despite the numerous benefits, virtual classroom teaching presents unique challenges that must be addressed. Issues such as digital divide, lack of face-to-face interaction, and varying levels of digital literacy can hinder the effectiveness of online education. Additionally, educators must develop new skills to effectively navigate and utilize these digital platforms. It is essential for institutions and policymakers to recognize these challenges and work collaboratively to create solutions that ensure equitable access to virtual learning.
As we move forward in an increasingly digital world, the collective responsibility lies with educators, institutions, and governments to enhance the quality and effectiveness of virtual classrooms. By investing in technology, training, and resources, we can maximize the transformative potential of virtual teaching, ensuring that future generations receive a robust and comprehensive education. Ultimately, the impact of virtual classrooms in education will continue to evolve, shaping the way knowledge is imparted and acquired in the years to come.